Alternators are the unsung heroes of modern vehicles. You may not give them much thought while driving, but they are vital in ensuring your car is always ready to go. In this guide, we’ll explore the mechanics of alternators and how they generate electrical power for your vehicle’s battery, starter motor and other systems. We’ll also explain how ls1 Alternator work with other car parts, like batteries and battery management systems (BMS).
Introduction: Understanding the Vital Role of Alternators
The alternator is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. It keeps you on the road, and it’s important to know how it works to tell if yours needs replacing.
So what exactly is an alternator? It’s a device that generates electrical power from mechanical energy (usually from your engine), stores it in batteries or capacitors, and then distributes that electricity back out again when needed for things like turning on lights or running other electronics.
There are two main types of alternators: permanent magnet (PM) and rotating field (RF). PM units use magnets fixed directly onto their rotors; RF units have electromagnets mounted around them instead. Both types produce alternating current (AC), which means they’re able to generate higher voltages than direct current (DC) devices such as batteries would allow without risking overheating themselves–and since they produce AC rather than DC voltage levels directly proportional to engine revolutions per minute (RPMs), they can also keep up with sudden changes in speed without stalling out like DC-powered systems would do under those circumstances!
How Do Alternators Generate Electrical Power?
Alternators are generators that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. A generator is a rotating electromagnet that can produce electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Alternator motors are used in automobiles, trucks and other vehicles to power the vehicle’s electrical system.
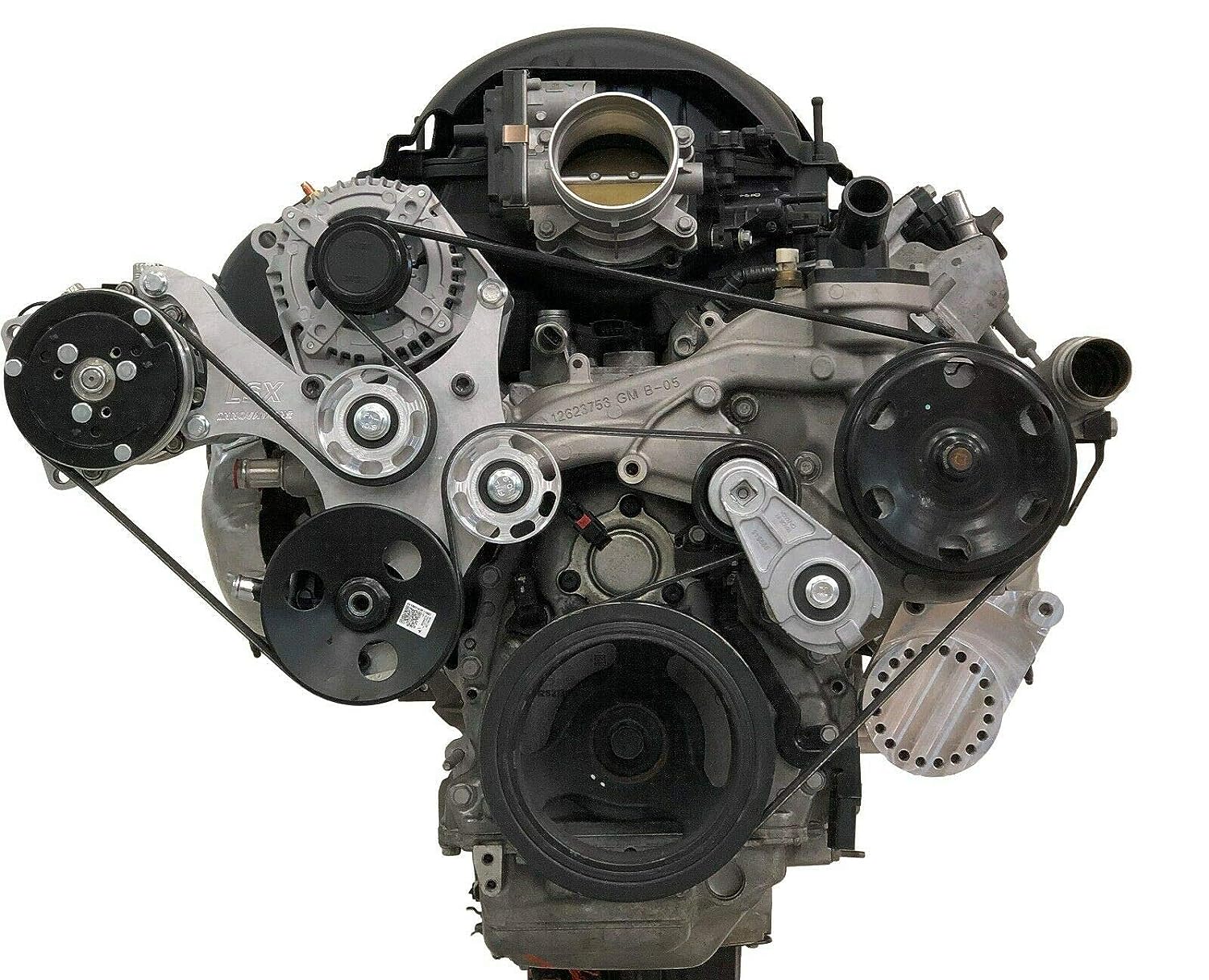
Alternators are made up of many components, including an armature (rotor), field winding(s) (stator) and rectifier assembly, as well as internal voltage regulator circuits that control output voltage levels based on engine RPMs
Key Components of an Automotive Alternator Explained
An automotive alternator consists of a rotor, stator and brushes. The rotor is made of soft iron, while the stator is made of hard steel. The meetings are copper, which connects your car’s battery to its electrical system.
The rotor is attached to the engine flywheel so that it spins when your engine turns over (i.e., starts). As this happens, magnets on both sides of its core generate electricity by passing through coils inside each end plate; these plates are then connected in series with other pieces inside your vehicle’s wiring harnesses (as shown above).
Alternator vs. Generator: Unraveling the Differences
One of the most common questions we hear from our readers is, “What’s the difference between a generator and an alternator?” The answer is pretty simple:
- Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, while alternators convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Generators are used in vehicles that don’t have batteries (like tractors), while alternators are used in vehicles with batteries (like cars).
If you’re wondering how this applies to your vehicle, check out the video above for a quick explanation of how alternators and generators work. If you want more information on the differences between alternators and generators, read on!
The Significance of Ls1 Alternator in Modern Vehicles
The ls1 Alternator is the heart of a car. It powers many of the vehicle’s electrical systems, including those that keep your battery running smoothly. In addition to powering your starter motor and other components, it provides power to your battery so you can start driving again when you’re ready–and even when you don’t want to!
It, alternators are essential components in any charging system; without them, there would be no way for vehicles with internal combustion engines (ICEs) or electric drivetrains (EDs) to recharge their batteries after use.
Common Signs of Alternator Problems and How to Diagnose Them
If you have a charging problem, it’s important to know the signs of alternator problems. If your car is having issues with starting or running, the first place to look is the battery and charging system. Here are some common signs that something may be wrong:
- Your battery gauge shows “E” for empty or less than 12 volts (when it should be 14).
- The headlights dim when turning on the wipers or A/C fan.
- The engine stalls when accelerating from a stop sign or traffic light. This can happen because there isn’t enough power left in the battery after starting up for additional loads like these two examples listed above!
DIY Alternator Maintenance: Tips to Keep It Running Smoothly
While the alternator is an integral part of your vehicle, mechanics and drivers often overlook it. As a DIYer, you can keep your alternators running smoothly with a few simple checks.
- Keep the alternator clean: If you’re regularly driving and have not had time to wash your car in a while, there’s no need to worry about washing off any dust or dirt that has collected on top of the alternator housing–but if there is visible grime or grease buildup around any electrical connections or hardware parts (such as pulleys), then give them a good wipe down with some WD-40 before moving forward.* Check belt wear: To check for excessive belt wear after cleaning off excess dirt/dust from the areas mentioned above, grab hold onto both ends of each belt (with fingers) while gently pulling downwards towards ground level until they reach the maximum stretch point without breaking off! If one side breaks before the other, then replace both sides together since they were probably installed backwards originally, which caused premature failure on one side first instead
Upgrading Alternators: Boosting Performance and Efficiency
You can upgrade an alternator to boost performance and efficiency. Upgrading an alternator is a great way to increase your vehicle’s power, but it’s important that you do it correctly or else you could end up damaging your vehicle.
There are many different upgrades available for alternators, including:
- Increased output capacity – This means that your new alternator will be able to produce more energy than before. This will allow you to charge batteries faster than before, so they won’t need charging as often during normal use!
- Lower internal resistance – This helps prevent overheating by reducing how much heat gets trapped inside the system when it’s working hard (like when starting up after being stored for a long time). It also improves performance at high speeds by reducing drag on other components, such as wiring harnesses; this allows them to work better under load conditions. More efficient cooling systems reduce stress on critical parts like bearings while increasing longevity through reduced wear-and-tear caused by excessive heat exposure.
Alternators and Battery Management Systems: A Symbiotic Relationship
As you know, alternators are an important part of automotive power. They generate electrical current and convert it into usable energy for your vehicle’s electrical system. However, two other components play key roles in this process: battery management systems (BMS) and alternator regulators.
A BMS regulates the flow of electricity between batteries and other components like headlights or stereo systems by controlling voltage levels at which they operate; if one was damaged or malfunctioned, it could cause problems with your vehicle’s electrical system–and even lead to a breakdown on the road! An alternator regulator controls how fast an alternator charges up its battery pack based on how much current is needed at any given time–you don’t want your car running out of juice while driving through town!
Eco-Friendly Alternators: Exploring Sustainable Energy Solutions
The alternator is a key engine component, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. It’s responsible for supplying power to your vehicle’s electrical system, which includes lights and other accessories.
An alternator converts rotational momentum into electrical energy using a magnetic field created by wire coils as they pass through a magnetic core (the stator). This process is called induction; it makes alternating current (AC) electricity instead of direct current (DC). AC electricity can be changed into DC using an inverter called an inverter–which is why you may have heard your alternator referred to as “an AC-to-DC converter.”
There are several different types of alternators available on the market today: permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), brushless DC machines (BLDCMs), shaded pole motors, and induction motors are all viable options depending on what kind of power needs need meeting by your vehicle – but one thing remains constant across all these technologies: they must be able to produce enough amperage at high speeds for them work effectively!
FAQs
Q: What is ls1 alternator?
A: An alternator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The main difference between an alternator and a generator is the voltage produced by each device. Generators produce electricity at low voltages while alternators output higher voltages, between 13-15 volts.
Q: How does an alternator work?
A: An alternating current (AC) flows through coils of wire wound around a magnetic core as they rotate inside of it, creating electromagnetic induction within those coils, which makes a voltage in your vehicle’s charging system that can be used to charge its battery or run other electrical components like headlights, stereo systems and air conditioners. When you start up your engine, it generates enough power to keep itself running until the engine reaches a normal operating temperature, at which point it switches over from being powered by steam pressure alone – called “cranking mode” – into “running mode” where combustion takes place within cylinders now hot enough for ignition purposes
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you understand alternators’ key role in automotive power systems. With so much going on inside these little devices, it’s no surprise they can be tricky to diagnose when they go wrong. But with the right knowledge and tools, even beginners can easily troubleshoot an alternator problem!